
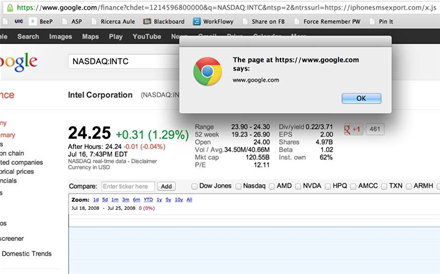
Google has paid a researcher $5000 for a cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the Google domain.
Italian computer engineer Michele Spagnuolo who received the bug bounty said the vulnerability needed no user interaction and was "due to a glitch in Google Finance" related to a JavaScript chart application (finance/f/sfe-opt.js).
"[It tricks] the JavaScript application for plotting charts to load a file hosted on an external domain and eval() its content as Javascript code," Spagnuolo said.
"This exploit does not require any user interaction, it's just a matter of clicking on a URL."
He said the vulnerability was fixed within days and offered steps to reproduce the XSS on his blog.
Cross-site scripting attacks were common and involved malicious scripts injected into web sites. They could occur whereever web applications incorporated user input in generated output without validation.


_(36).jpg&h=140&w=231&c=1&s=0)
_(23).jpg&h=140&w=231&c=1&s=0)
_(28).jpg&h=140&w=231&c=1&s=0)





 iTnews Executive Retreat - Security Leaders Edition
iTnews Executive Retreat - Security Leaders Edition
 iTnews Cloud Covered Breakfast Summit
iTnews Cloud Covered Breakfast Summit
 The 2026 iAwards
The 2026 iAwards












_(1).jpg&h=140&w=231&c=1&s=0)



